

|
|
|
|
The
Palestinian Territories in Brief
[Geography and Demography
Context]
[Palestinian Economy
|
Geography and Demography context
|
The Palestinian territories are divided into two
entities: the North Governorates and the South Governorates known before as the
West Bank and the Gaza Strip respectively.
The Gaza Strip (365 km2) is a narrow strip stretching along
the East south edge of the Mediterranean. It lies on longitude 34˙
26`
east and
altitude 31˙
10` north equator with width ranging from 5-12 km. According to the
1997 figures, the population of the Gaza Strip reached 1,023,095 inhabitants,
which makes it highly populated (2800 inh/km2). On the other hand,
the West Bank (5788 km2) which lies on longitude 35˙
12`
east and
altitude 31˙
31` north equator is situated on the central Highlands of Palestine.
The population of the West Bank reached 1,660,868 inhabitants, which
indicates a relatively low density of 280 inh/km2.
The high average population growth in Palestine (6.12 % per annum in the
Gaza Strip and 5.61% per annum in the West Bank in mid. 1997) is a considerable
factor in electricity demand for Palestine.
Palestinian Economy
|
Palestinian Territories were affected from the
political unrest during the past 50 years in the area. Economic and social
patterns were deprived from noticeable development and remained primitive
especially during the Israeli occupation period. The current per capita average
income in Palestine is about 1340 USD/year.
Climatic context
|
The Palestinian Territories are located in a transitional climatic zone between the Mediterranean and the arid tropical zones. Palestineĺs climatic conditions vary widely. The Palestinian Territories could be divided into three climatic zones: coastal areas, hilly areas and Jordan valley. The coastal climate (in the Gaza Strip and the northwestern part of the West Bank) is hot and humid during the summer and mild during the winter. In the hilly areas of the West Bank, cold winter conditions and mild summer weather prevail. The climate in the Jordan valley is hot and dry in summer and warm and humid during the winter.
Daily average temperatures in the coastal areas
are 24 ░C
and 15 ░C
in summer and winter respectively. In the hilly areas of the West Bank
temperatures occasionally drop to 0░C
but they are usually less by 1-3░C
than in coastal areas, while it is always higher in the Jordan valley.
Temperature in the Jordan Valley can rise in summer to 45░C
with an annual average of 24░C.
Solar insulation in Palestine
|
Solar insulation has an annual average of 5.4
kWh/m2.day, which fluctuates significantly during the day and all
over the year, and approximately 2860 mean-hour sunshine throughout the year.
The measured values in the different areas show that the annual average
insulation values are about 5.24 kWh/m2.day, 5.63 kWh/m2.day,
5.38 kWh/m2.day in the coastal area, hilly area and Jordan valley
respectively. The following figure shows the annual monthly averages solar
radiation amounts in the three climatic zones.
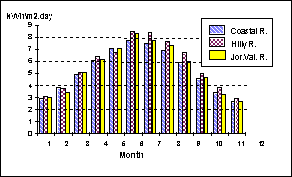
Annual monthly
average variation in solar radiation in the three Climate zones of the
Palestinian Territories
Consumption and Demand
1995-1998
|
In the Palestinian
Territories
|
Table
1: Consumption and demand in the Gaza Governorates
|
Year |
Consumption
(GWh) |
Max
Demand (MW) |
Load
Factor (%) |
|
1995 |
487.1 |
94.1 |
59.1 |
|
1996 |
502.6 |
93.1 |
61.6 |
|
1997 |
546.4 |
102.5 |
60.8 |
|
1998 |
598.9 |
106.3 |
64.3 |
Table
2: Consumption and demand in the West Bank
|
Year |
Consumption
(GWh) |
Max
Demand (MW) |
Load
Factor (%) |
|
1995 |
1008 |
199 |
57.8 |
|
1996 |
1104 |
218 |
57.8 |
|
1997 |
1223 |
244 |
57.2 |
|
1998 |
1411 |
274 |
58.8 |
The gap between supply and demand is growing rapidly as economic activity increases. There is suppressed demand and a growing backlog of requests for new connections. The suppressed demand is mainly due to the physical constraints of the existing nine feeders. The technical teams of the PEA and the municipalities rehabilitated 70% of the network. These projects were financed by the Norwegian grant with a total cost of 23MUSD. In the Gaza Governorates, the executed projects in the northern area costed about 5.64 MUSD with an installed capacity of 41.47 MVA and 6.5 MVAR. The length of the network reached 45km. On the other hand, the planned projects are estimated at 3.31MUSD, and the capacity to be installed will be 24.42MVA with a total network length of 28.9km.
In
the south area of the Gaza Governorates, the projects executed costed 5.1MUSD
with an installed capacity of 32.4MVA, 3.5 MVAR. The network length reached 56km.
|
| |
|
Consumption and demand in Gaza Governorates (Need MS Excel program) | |
|
maximam Demand in Gaza Strip . MW (Need MS Excel program) |
|
E-Mail : pea@palnet.com
Main Office PEA. : Gaza -P.O Box 3041/ Tel: 972-7-2821702 , Fax : 972-7-2824849 Al-Bireh-P.O. Box:3591 / Tel: 972-2- 2986190/2 , Fax:972-2-2986191
|